YAP Documentation
YAP - Yet Another (natural language) Parser
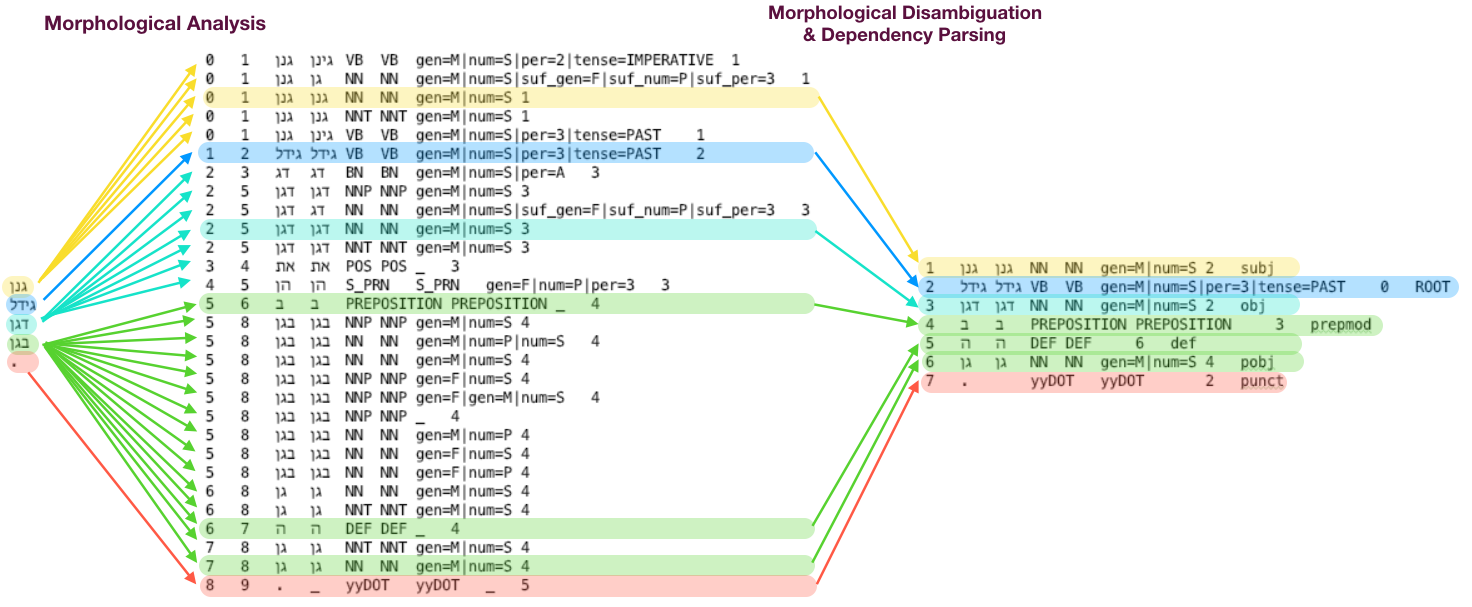
How it Works
In MRLs, each token may have multiple different morphological analyses, where only one is relevant in context. This morphological ambiguity is represented by a word-lattice describing the various morpheme sequences that may combine to form it, with only one sequence suited in the context of the sentence.Morphological Disambiguation (MD) is particularly difficult in MRLs due significant morphological richness.
YAP provides a framework (currently supporting Modern Hebrew) that does lexicon-based morphological analysis followed by a joint morph-syntactic disambiguation and dependency parsing.
Input
YAP works on the tokenized sentence level,meaning that the input to YAP is a list of tokens:
גנן
גידל
דגן
בגן
.
Output
Morphological Analysis Lattice:
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=2|tense=IMPERATIVE 1
0 1 גנן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 1
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גנן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דג דג BN BN gen=M|num=S|per=A 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דג NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 3
2 5 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 את את POS POS _ 3
4 5 הן הן S_PRN S_PRN gen=F|num=P|per=3 3
5 6 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=P 4
6 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
6 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
6 7 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
7 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
7 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
8 9 . _ yyDOT yyDOT _ 5
Morphological Disambiguation Lattice:
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
4 5 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
5 6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
6 7 . _ yyDOT yyDOT _ 5
Dependency Parse Tree:
1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 subj _ _
2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 0 ROOT _ _
3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 obj _ _
4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION 3 prepmod _ _
5 ה ה DEF DEF 6 def _ _
6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4 pobj _ _
7 . yyDOT yyDOT 2 punct _ _
Quick Start
YAP can run on Windows, Linux and MacOS. Windows users: YAP doesn't handle Windows style text files that have BOM marks and CRLF newlines. So if you're running on Windows and YAP doesn't work make sure you don't have CRLF line endings and no BOM mark.Requirements
Compilation
The following instructions are for Linux but similarly this can be done on Windows and MacOS.- Make sure you have Go and Git installed and on the command PATH.
- Setup a Go environment:
- Create a directory (usually per workspace/project)
mkdir yapproj; cd yapproj - Set
$GOPATHenvironment variable to your workspace:export GOPATH=path/to/yapproj - In the workspace directory create the src subdirectory:
mkdir src - cd into the src directory
cd src - Clone the repository in the src folder of the workspace
git clone https://github.com/OnlpLab/yap.git - Unzip the models and build the application:
$ cd yap
$ bunzip2 data/*.bz2
$ go get .
$ go build .
$ ./yap
./yap - invoke yap as a standalone app or as an api server
Commands:
api start api server
dep runs dependency training/parsing
hebma run lexicon-based morphological analyzer on raw input
joint runs joint morpho-syntactic training and parsing
ma run data-driven morphological analyzer on raw input
malearn generate a data-driven morphological analysis dictionary for a set of files
md runs standalone morphological disambiguation training and parsing
Use "./yap help <command>" for more information about a command
Running YAP from the command line
From the command line you can process one input file at a time. It is possible to have multiple sentences in a single file.Input File
One token per line (including punctuation), empty line separating sentences.THE LAST LINE IN THE FILE MUST BE EMPTY:
$ cat input.txt
גנן
גידל
דגן
בגן
.
Processing a file
1. Morphological Analysis - given the input tokens, generate the ambiguous lattices:
$ ./yap hebma -raw input.txt -out input.lattice
2. Morphological Disambiguation and Dependency Parsing - given the input ambiguous lattices, disambiguate and parse:
$ ./yap joint -in input.lattice -os output.segmentation -om output.mapping -oc output.conll
Output Files
1. Morphological Analysis:
$ cat input.lattice
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=2|tense=IMPERATIVE 1
0 1 גנן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 1
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גנן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דג דג BN BN gen=M|num=S|per=A 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דג NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 3
2 5 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 את את POS POS _ 3
4 5 הן הן S_PRN S_PRN gen=F|num=P|per=3 3
5 6 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=P 4
6 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
6 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
6 7 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
7 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
7 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
8 9 . _ yyDOT yyDOT _ 5
2. Morphological Disambiguation:
$ cat output.mapping
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
4 5 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
5 6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
6 7 . _ yyDOT yyDOT _ 5
3. Dependency Tree:
$ cat output.conll
1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 subj _ _
2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 0 ROOT _ _
3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 obj _ _
4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION 3 prepmod _ _
5 ה ה DEF DEF 6 def _ _
6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4 pobj _ _
7 . yyDOT yyDOT 2 punct _ _
Running YAP as a RESTful API server
1. YAP can run as a server listening on port 8000:
$ ./yap api
2. You can then send HTTP GET requests with json objects in the request body and receive back a json object containing the 3 output levels:
$ curl -s -X GET -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"text": "גנן גידל דגן בגן "}' localhost:8000/yap/heb/joint | jq .
{
"ma_lattice": "0\t1\tגנן\tגינן\tVB\tVB\tgen=M|num=S|per=2|tense=IMPERATIVE\t1\n0\t1\tגנן\tגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3\t1\n0\t1\tגנן\tגנן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t1\n0\t1\tגנן\tגנן\tNNT\tNNT\tgen=M|num=S\t1\n0\t1\tגנן\tגינן\tVB\tVB\tgen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST\t1\n1\t2\tגידל\tגידל\tVB\tVB\tgen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST\t2\n2\t3\tדג\tדג\tBN\tBN\tgen=M|num=S|per=A\t3\n2\t5\tדגן\tדגן\tNNP\tNNP\tgen=M|num=S\t3\n2\t5\tדגן\tדג\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3\t3\n2\t5\tדגן\tדגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t3\n2\t5\tדגן\tדגן\tNNT\tNNT\tgen=M|num=S\t3\n3\t4\tאת\tאת\tPOS\tPOS\t_\t3\n4\t5\tהן\tהן\tS_PRN\tS_PRN\tgen=F|num=P|per=3\t3\n5\t6\tב\tב\tPREPOSITION\tPREPOSITION\t_\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNNP\tNNP\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=P|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNNP\tNNP\tgen=F|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNNP\tNNP\tgen=F|gen=M|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNNP\tNNP\t_\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=P\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=F|num=S\t4\n5\t8\tבגן\tבגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=F|num=P\t4\n6\t8\tגן\tגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n6\t8\tגן\tגן\tNNT\tNNT\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n6\t7\tה\tה\tDEF\tDEF\t_\t4\n7\t8\tגן\tגן\tNNT\tNNT\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n7\t8\tגן\tגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n\n",
"md_lattice": "0\t1\tגנן\tגנן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t1\n1\t2\tגידל\tגידל\tVB\tVB\tgen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST\t2\n2\t3\tדגן\tדגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t3\n3\t4\tב\tב\tPREPOSITION\tPREPOSITION\t_\t4\n4\t5\tה\tה\tDEF\tDEF\t_\t4\n5\t6\tגן\tגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t4\n\n",
"dep_tree": "1\tגנן\tגנן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t2\tsubj\t_\t_\n2\tגידל\tגידל\tVB\tVB\tgen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST\t0\tROOT\t_\t_\n3\tדגן\tדגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t2\tobj\t_\t_\n4\tב\tב\tPREPOSITION\tPREPOSITION\t\t2\tprepmod\t_\t_\n5\tה\tה\tDEF\tDEF\t\t6\tdef\t_\t_\n6\tגן\tגן\tNN\tNN\tgen=M|num=S\t4\tpobj\t_\t_\n\n"
}
$ curl -s -X GET -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"text": "גנן גידל דגן בגן "}' localhost:8000/yap/heb/joint | jq '.ma_lattice, .md_lattice, .dep_tree' | sed -e 's/^.//' -e 's/.$//' -e 's/\\t/\t/g' -e 's/\\n/\n/g'
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=2|tense=IMPERATIVE 1
0 1 גנן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 1
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גנן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 1
0 1 גנן גינן VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דג דג BN BN gen=M|num=S|per=A 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דג NN NN gen=M|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_num=P|suf_per=3 3
2 5 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
2 5 דגן דגן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 את את POS POS _ 3
4 5 הן הן S_PRN S_PRN gen=F|num=P|per=3 3
5 6 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP gen=F|gen=M|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NNP NNP _ 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=M|num=P 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=S 4
5 8 בגן בגן NN NN gen=F|num=P 4
6 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
6 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
6 7 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
7 8 גן גן NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
7 8 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
0 1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 1
1 2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 2
2 3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 3
3 4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
4 5 ה ה DEF DEF _ 4
5 6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
1 גנן גנן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 subj _ _
2 גידל גידל VB VB gen=M|num=S|per=3|tense=PAST 0 ROOT _ _
3 דגן דגן NN NN gen=M|num=S 2 obj _ _
4 ב ב PREPOSITION PREPOSITION 3 prepmod _ _
5 ה ה DEF DEF 6 def _ _
6 גן גן NN NN gen=M|num=S 4 pobj _ _
7 . yyDOT yyDOT 2 punct _ _
Joint vs Pipeline
The joint morph-syntactic framework has been shown to improve both morphological disambiguation as well as dependenyc parsing accuracy compared to a pipeline architecture where morphological disambiguation runs independently and then dependency parsing runs given the disambiguated lattice. While the joint framework should be used in general, it is possible to run YAP in a pipeline fashion, in which case processing is done in 3 steps: 1. Morphological Analysis - same as for the joint processing flow:
$ ./yap hebma -raw input.txt -out input.lattice
2. Morphological Disambiguation - given the input ambiguous lattices, output the disambiguated lattice:
$ ./yap md -in input.lattice -om output.mapping
3. Dependency Parsing - given the disambiguated lattice, output the dependency tree:
$ ./yap dep -inl output.mapping -oc output.conll
FAQ
1. Lattice file format
A lattice file is a graph representation where every path in the graph is a possible sequence of morphemes. Each line in the lattice file is an edge in the graph:- FROM
- Index of the outgoing vertex of the edge
- TO
- Index of the incoming vertex of the edge
- FORM
- word form or punctuation mark
- LEMMA
- Lemma of the word form; underscore if not available
- CPOSTAG
- Coarse-grained part-of-speech tag; underscore if not available
- POSTAG
- Fine-grained part-of-speech tag; underscore if not available; in YAP both POSTAG and CPOSTAG are always identical
- FEATS
- List of morphological features separated by a vertical bar (|) from a pre-defined language-specific inventory; underscore if not available
- TOKEN
- Source token index
2. CoNLL file format
The CoNLL format is used to represent dependency trees. Each line represents a node in the tree:- ID
- Morpheme index, starting at 1 for each new sentence
- FORM
- Word form or punctuation mark
- LEMMA
- Lemma of word form; underscore if not available
- CPOSTAG
- Coarse-grained part-of-speech tag; underscore if not available
- POSTAG
- Fine-grained part-of-speech tag; underscore if not available; in YAP both POSTAG and CPOSTAG are always identical
- FEATS
- List of morphological features separated by a vertical bar (|) from a pre-defined language-specific inventory; underscore if not available
- HEAD
- Head of the current morpheme, which is either a value of ID, or zero (’0’) if the token links to the virtual root node of the sentence. There may be multiple tokens with a HEAD value of zero.
- DEPREL
- Dependency relation to the HEAD. The dependency relation of a token with HEAD=0 is simply ’ROOT’
- PHEAD
- Projective head; Not relevant - YAP doesn't use it
- PDEPREL
- Dependency relation to the PHEAD; not relevant - YAP doesn't use it
3. How to tokenize
As mentioned above, YAP expects the input as a list of tokens. This means that the user is responsible for tokenization. The simplest and most straight forward tokenizaion can be done by simply separating words with white space between them. While this approach is fine for running a few test cases it might not work well in general. Some tokenizers that are available and work with Modern Hebrew are:Publications
A paper on the morphological analysis and disambiguation aspect for Modern Hebrew and Universal Dependencies was presented at COLING 2016. The complete joint morphosyntactic model, along with benchmark experiments and error analysis are available in a TACL paper accepted for publication in 2018, to be uploaded soon. yap was also used for parsing Hebrew, as well as many other languages, in the following academic studies:- NLP lab at the CoNLL shared Task on Raw-to-Dependencies parsing at CoNLL 2017
- The ONLP lab at the CoNLL shared Task on Raw-to-Dependencies parsing at CoNLL 2018
- The Hebrew Universal Dependencies Treebank at UDW 2018
- Neural Sentiment Analysis for Hebrew at COLING 2018
Licensing Highlights
- ode is provided with a permissive license (apache 2.0), as is, and without warranties.
- ata and lexicon the parser uses belong to MILA at the Technion
- production* use, please check with Prof. Alon Itay from The technion data/lexicon license conditions.
Citation
If you make use of this software for research, we would appreciate the following citation:
@InProceedings{moretsarfatycoling2016,
author = {Amir More and Reut Tsarfaty},
title = {Data-Driven Morphological Analysis and Disambiguation for Morphologically Rich Languages and Universal Dependencies},
booktitle = {Proceedings of COLING 2016},
year = {2016},
month = {december},
location = {Osaka}
}
@inproceedings{adler06,
Author = {Adler, Meni and Elhadad, Michael},
Booktitle = {ACL},
Crossref = {conf/acl/2006},
Editor = {Calzolari, Nicoletta and Cardie, Claire and Isabelle, Pierre},
Ee = {http://aclweb.org/anthology/P06-1084},
Interhash = {6e302df82f4d7776cc487d5b8623d3db},
Intrahash = {c7ac3ecfe40d039cd6c9ec855cb432db},
Keywords = {dblp},
Publisher = {The Association for Computer Linguistics},
Timestamp = {2013-08-13T15:11:00.000+0200},
Title = {An Unsupervised Morpheme-Based HMM for {H}ebrew Morphological
Disambiguation},
Url = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/acl/acl2006.html#AdlerE06},
Year = 2006,
Bdsk-Url-1 = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/acl/acl2006.html#AdlerE06}}